
|
Defines | |
| #define | warppath_CHECK(flag, w) |
| is w a warppath? | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | SlopeConstraint { SLOPE_CONSTRAINT_NONE = 0, SLOPE_CONSTRAINT_LAX, SLOPE_CONSTRAINT_MEDIUM, SLOPE_CONSTRAINT_SEVERE } |
Severity of the slope constraint in the Dynamic Time-Warping Alg. More... | |
Functions | |
| Array * | dtw_add_signals (const Array *s1, const Array *s2, const Array *path, OptArgList *opts) |
| Add signals according to a warppath. | |
| Array * | matrix_dtw_backtrack (const Array *d) |
| calculate the warping path. | |
| Array * | matrix_dtw_cumulate (Array *mat, bool alloc, OptArgList *optargs) |
| cumulate a distance matrix d for Dynamic Time-Warping. | |
Detailed Description
STATUS: stable Warping functions.
Example for warping 2D data:
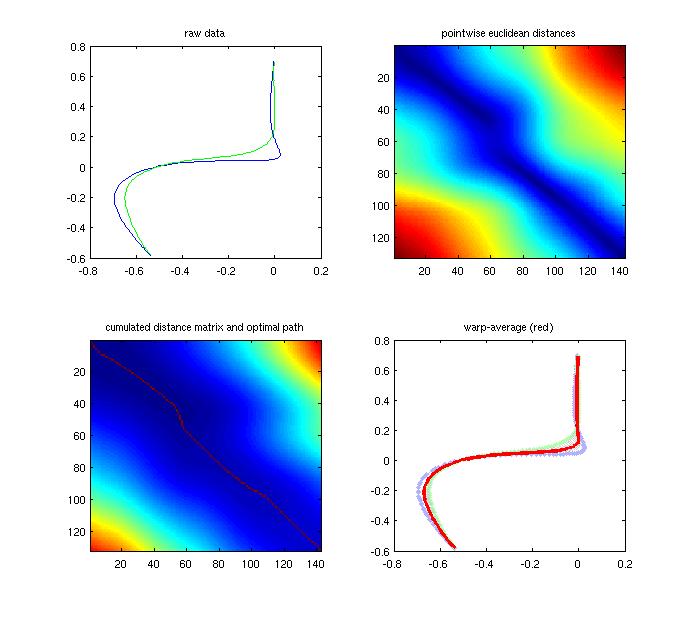
- pardtw Dynamic Time Warping
Dynamic Time-Warping is a method to account for temporal distortion when comparing two signals. It is done by finding a function that minimizes the sum of entries through a distance matrix, such that
![\[ \mbox{argmin}_\phi \int d(s_1(t_1),s_2(\phi(t_2))) \]](form_84.png)
for a given pointwise distance between two signals. Such distances can be computed using the functions in distances.h.
The minimization is done by cumulating the matrix
![\[ D_{jk} = \mathbf{d}_{jk}+min{\{D_{j,k-1}, D_{j-1,k}, D_{j-1, k-1}\}} \]](form_85.png)
and backtracking via the minimum of the three neighboring entries (down, down-right, right) from to
to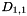 . Here, the functions dtw_cumulate_matrix() and dtw_backtrack() do that.
. Here, the functions dtw_cumulate_matrix() and dtw_backtrack() do that.
Finally, the signals need to be mapped to one another to get time-amplitude averaging with
![\[ s'(t)=\frac{\omega_1 s_1(p_1^t) + \omega_2 s_2(p_2^t)}{\omega_1 + \omega_2} \]](form_86.png)
using weights . Here, you can use warp_add_signals_by_path().
. Here, you can use warp_add_signals_by_path().
Define Documentation
| #define warppath_CHECK | ( | flag, | ||
| w | ||||
| ) |
if(!( (w)->ndim==2 && (w)->dtype==UINT )){ \ char *dts=""; \ array_DTYPESTRING( dts, w->dtype ); \ errprintf("not a warppath, ndim=%i, dtype=%s\n", w->ndim, dts ); \ flag=FALSE; \ } else { flag=TRUE; }
is w a warppath?
Usage:
bool ispath; warppath_CHECK( ispath, X ); if( !ispath ) return NULL;
- Parameters:
-
flag (output) (bool) set by macro w (input) Array* to check
Enumeration Type Documentation
| enum SlopeConstraint |
Function Documentation
| Array* dtw_add_signals | ( | const Array * | s1, | |
| const Array * | s2, | |||
| const Array * | path, | |||
| OptArgList * | opts | |||
| ) |
Add signals according to a warppath.
If called from hierarchical averaging routines, you might want to pass a "weights" field in the optional arguments.
- Parameters:
-
s1 N1 x p (DOUBLE) array; first signal s2 N2 x p (DOUBLE) array; second signal path - contains warppath (2xN INT); opts may contain: - "weights=double*" - weights in average, for using it with hierarchical averaging; should be 2 double values with w[0]+w[1]=1.0
- Returns:
- the warped average of the signals; N1+N2 samples
calculate the warping path.
- Parameters:
-
d is the cumulated distances matrix (usually output from matrix_dtw_cumulate())
- Returns:
- the warp-Path (2D uint array, 2 x N)
| Array* matrix_dtw_cumulate | ( | Array * | mat, | |
| bool | alloc, | |||
| OptArgList * | optargs | |||
| ) |
cumulate a distance matrix d for Dynamic Time-Warping.
![\[ D_{jk} = d_{jk}+\min{\{D_{j,k-1}, D_{j-1,k}, D_{j-1, k-1}\}} \]](form_79.png)
The formula is modified, depending on the slope constraint.
- Parameters:
-
mat distance matrix alloc if TRUE, output matrix is freshly allocated; else mat is overwritten optargs may contain: - "slope_constraint=int" slope constraint, one of SLOPE_CONSTRAINT_*; default=SLOPE_CONSTRAINT_NONE
 1.7.0
1.7.0